Industry
 Num:32
Num:32 See:3582
See:35822020-10
09
Hardware necessary skills, MOS tube composed of basic gate logic circuit
This article shares the following key points:
- OD gate is a very important concept of digital circuit, which is composed of Buffer and drain open circuit.
- Inverters, lines and logic how to play, and how to use?
- Apply typical circuits to understand basic logic gates, and gates, or gates, and non gates, based on schematic diagrams and truth tables.
- What about semiconductor SS, TT, FF?
1. MOS tube logic circuit (and gate, or gate, non-gate, etc.)
As a hardware engineer, you can't help but understand chips. In order to understand the chip, the basic logic circuits composed of MOS tubes must be memorized so as to be able to understand the chip block diagram more proficiently. The field-effect Transistor provides a variety of gate circuits that can be visualized in a variety of combinations or visuals that, as the description in the beginning, may be the basis of a modern IC. The following circuit forms exist in a large number of commonly used 74 series chips, and the OD gate introduced later, buffers are commonly seen in the chip GPIO port and other pin design.
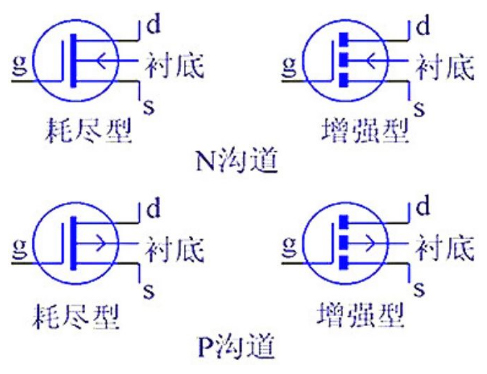
MOS tube constitutes the basic gate, or gate circuit
And the door can be composed of six tubes, the schematic diagram should be more clear to see the work diagram with the door, and then the truth table can see the corresponding relationship between the input and output. In this paper, the corresponding circuit with the gate is given. If you are interested, you can think about the circuit structure of the gate. In fact, there is a corresponding relationship between the two.

2. The inverter
The diagram below shows the circuit diagram of the inverter. The input and output states are opposite, which is called the inverter.
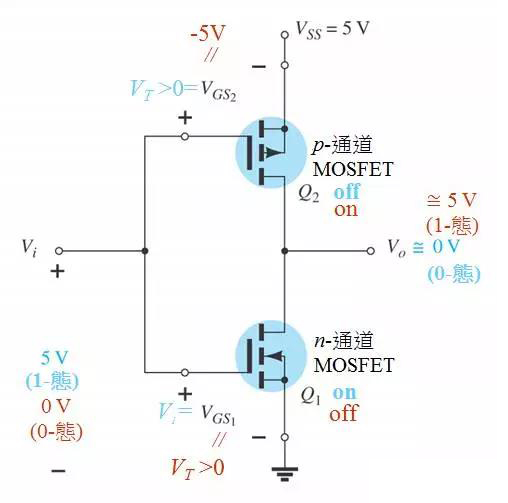
Circuit analysis:
The input Vi is low power, the upper tube is on, the lower tube is off, and the output is high level. The input Vi is high level, the upper tube is off, the lower tube is on, and the output is low level.
Nand gate:
The diagram below shows the circuit diagram of and not gate, which is equal to zero and different to one.
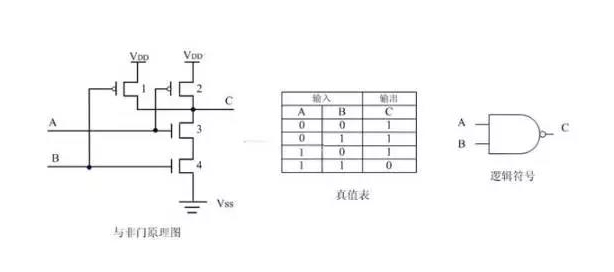
When A and B inputs are all at low power, 1,2 tubes are on and 3,4 tubes are off. The voltage at terminal C is consistent with VDD and high level is output. When A input high level, B input low level, 1,3 tube conduction, 2,4 tube cutoff, the potential at the C end is consistent with the drain of 1 tube, output high level. When A input low level, B input high level, 2,4 conduction, 1,3 tube cutoff, C end potential and 2 tube drain are consistent, output high level. When A and B inputs are all at high voltage, 1 and 2 tubes are off, 3 and 4 tubes are on, the voltage at C terminal is consistent with the ground, and the output is low level.
4. Buffer
CMOS buffer (buffer), buffer and inverter is the opposite, buffer input and output are the same, inverter input and output are opposite.
4. Buffer
CMOS buffer (buffer), buffer and inverter is the opposite, buffer input and output are the same, inverter input and output are opposite.

Circuit analysis:
The first stage Q1, Q2 constitutes an inverter; The latter stage Q3, Q4 constitutes a phase inverter, which is equivalent to inverting the phase twice, so it is reduced again.
5. Drain open door
Drain open door is a very classic circuit, commonly seen in the main chip GPIO port or single-chip GPIO port design. The most important point to note is that the open drain state is a high resistance state, which generally requires a pull resistor.
The first stage Q1, Q2 constitutes an inverter; The latter stage Q3, Q4 constitutes a phase inverter, which is equivalent to inverting the phase twice, so it is reduced again.
5. Drain open door
Drain open door is a very classic circuit, commonly seen in the main chip GPIO port or single-chip GPIO port design. The most important point to note is that the open drain state is a high resistance state, which generally requires a pull resistor.

(Application of drain Open Door - Line and Logic)Z=z1z2z3
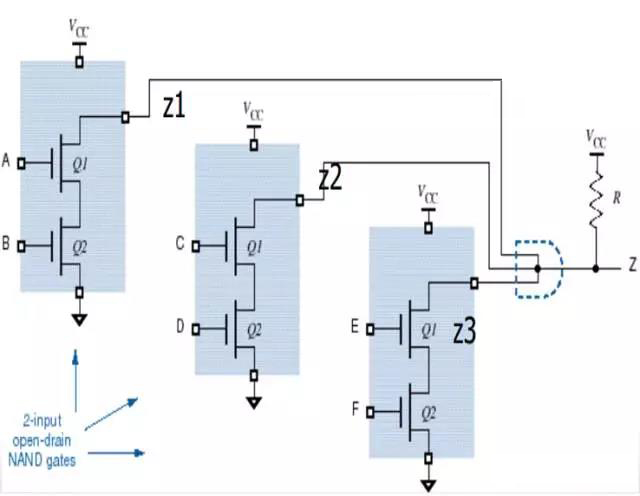

The reason for "line and" logic is that the audion output from multiple logic units share a pull up resistor. As long as one logic unit outputs low level, that is, the collector (drain) open output tube conduction, then the low level is output. Only all the units are cut off, and the output end is set to high level by the pull-up resistor. This is a very practical circuit, which can be used in logic arbitration and other circuit systems.
Perhaps after a few years of work, the general will feel that the transistor circuit is very simple, that can only show that the research is not deep enough. Sometimes the simpler things are the more complicated things at the bottom. For example, from the point of view of technology, the transistor is divided into TT, SS, FF, IC design is not around these, the basic is not easy, considering more in-depth, but I think only scratch the surface.

Share





站LOGO.png)





.jpg)